Rotation, in the context of music production, typically refers to a technique or process used to alter or modulate various aspects of a musical composition.
Function:
Rotation involves changing or shifting elements within a musical piece, such as rhythm, melody, harmony, or instrumentation, to create variation and maintain interest.
It can encompass techniques like rhythmic displacement, melodic inversion, chord substitutions, and changes in instrumentation or arrangement.
Rotation can occur on different levels, from subtle variations within a single musical phrase to broader transformations across entire sections of a composition.
Characteristics:
Creativity: Rotation encourages creative experimentation with musical elements, allowing composers and producers to explore different permutations and variations within their compositions.
Dynamism: By introducing changes and variations, rotation adds dynamism and movement to a musical piece, preventing it from becoming repetitive or monotonous.
Flexibility: Rotation can be applied to various musical genres and styles, from classical to electronic music, offering flexibility and adaptability in the composition process.
Highlights:
Musical Development: Rotation facilitates the development and evolution of musical ideas by presenting them in new contexts and arrangements.
Expressiveness: It allows composers and producers to express their artistic vision by manipulating and transforming musical elements to achieve desired emotional or aesthetic effects.
Continuity and Unity: Despite introducing changes, rotation can help maintain continuity and unity within a composition by retaining certain thematic elements or motifs while exploring different variations.
Advantages:
Variation: Rotation adds variety and interest to a musical piece, keeping listeners engaged and preventing it from feeling static or repetitive.
Innovation: By encouraging experimentation and exploration, rotation can lead to innovative and unique musical ideas, pushing the boundaries of conventional composition techniques.
Coherence: When used effectively, rotation can contribute to the coherence and coherence of a composition by balancing familiarity with novelty, creating a satisfying listening experience for the audience.

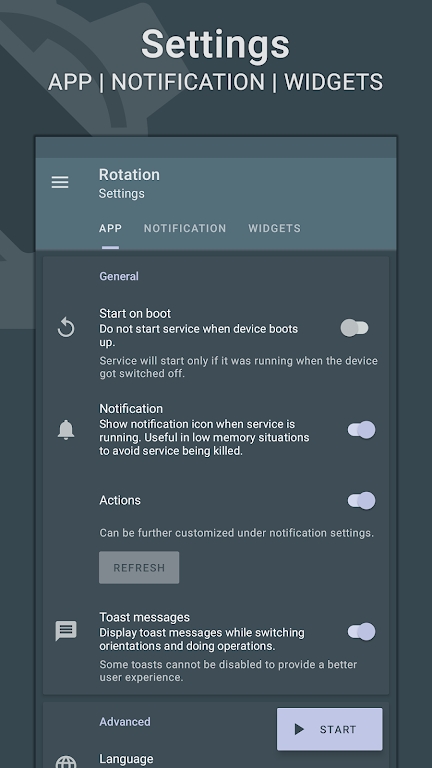
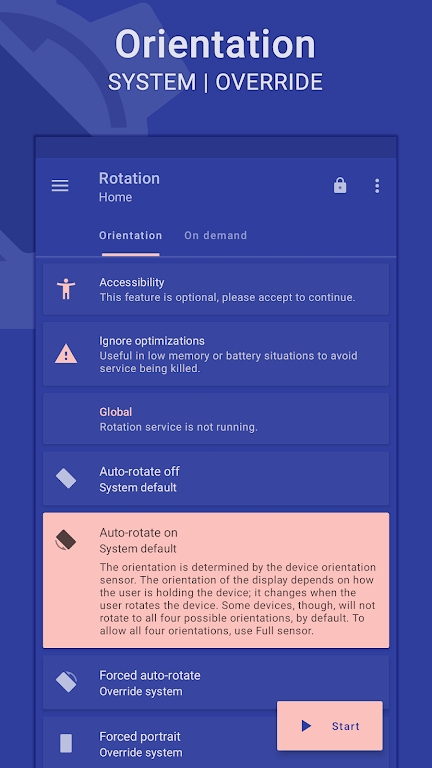
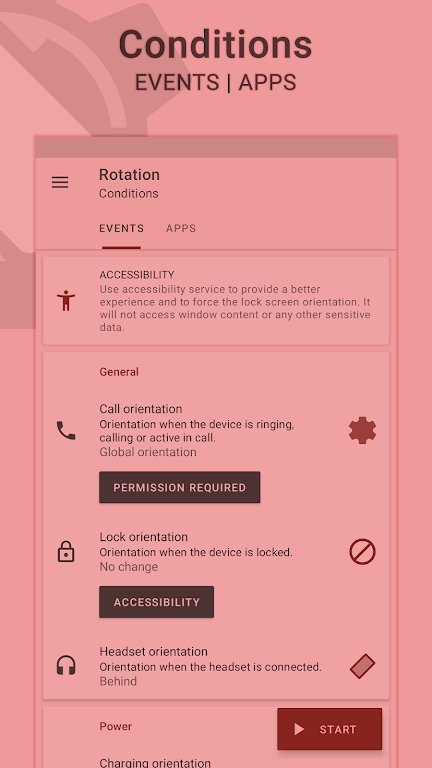
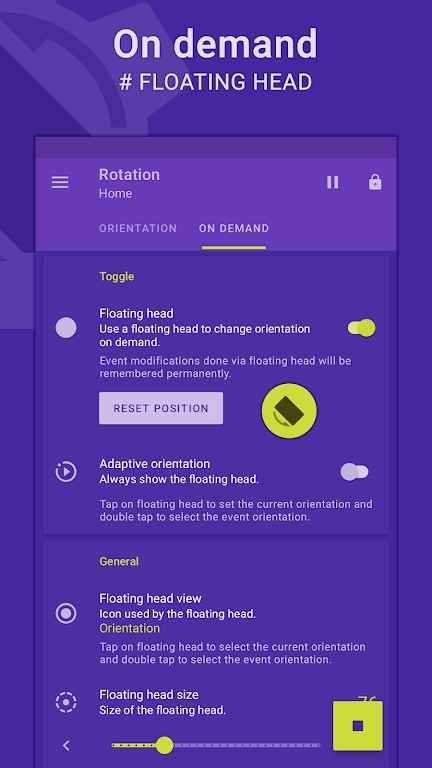

















Preview: